|
|
|
|
|
The Gum Recession Project
www.gumrecession.com
"Keeping Your Smile for a Lifetime"
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
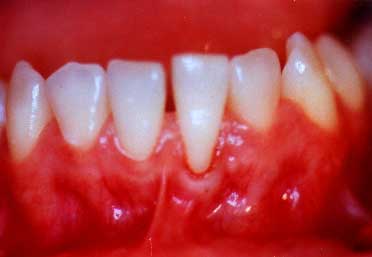
Gum Recession
(Thin, Fragile Tissue)
|
|
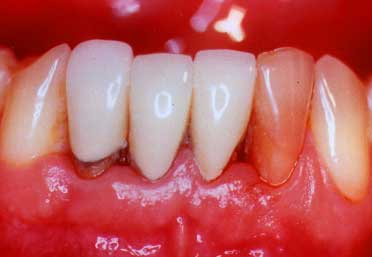
Gum Recession
(Bacterial Infection)
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Gum recession is one of the gum problems that patients can frequently identify. When the recession is in the front of the mouth, it may be readily seen -- especially if it is on the upper front teeth. However, recession may occur on any of the teeth, and on either the lip/cheek side of the teeth or the tongue side or roof-of-the mouth side of the teeth. There are two different types of recession that we will address. One is the type that occurs in patients' mouths when patients are usually doing a very good job of cleaning their teeth. This type of recession is usually related to the patient being pre-disposed towards recession due to the gums being thin and fragile. We will describe this as Gum Recession: Thin, Fragile Tissue.
Another type of recession is seen by patients who have gum disease that is a bacterial infection resulting from the bacteria that are normally in the mouth. This is a different type of recession and involves not only gum recession, but also the destruction of the underlying bone which supports the teeth. While the patient may see some gum recession, if they are aware of the signs of gum disease (periodontitis), they should see other signs as well as the recession. This type of recession we will describe as Gum Recession: Bacterial Infection.
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
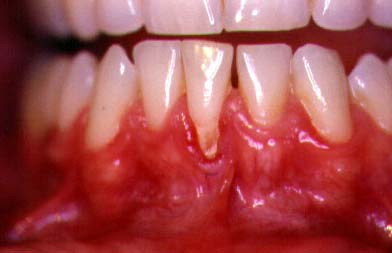
Gum Recession
(Thin, Fragile Tissue)
The root of the tooth is exposed due to the lack of thick, tough tissue ("attached gingiva") and bone over the root of the tooth
|
|
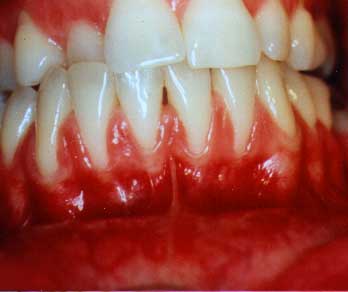
Gum Recession
(Thin, Fragile Tissue)
The recession is from very prominent roots (look at the "bulging roots" on the right)
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
Gum Recession: Thin, Fragile Tissue
The treatment of gum recession varies depending upon which type of recession is present. For Gum Recession: Thin, Fragile Tissue, the treatment of choice is Periodontal Plastic Surgery. Periodontal Plastic Surgery is predictable in creating thick, tough gum tissue (called "attached gingiva") which will prevent further recession, and in some cases will also cover the existing recession. An important point to understand is that these periodontal plastic surgical techniques have the treatment of recession as their primary treatment objective. The majority of treatment solutions that are discussed in this gumrecession.com site will relate to treating this type of recession by stopping further recession and sometimes covering existing recession.
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
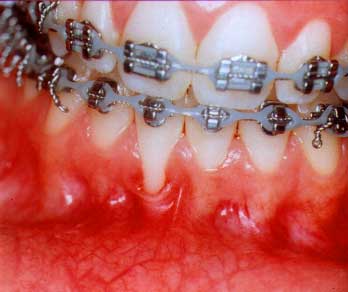
Pre-Treatment
Gum Recession
(Thin, Fragile Tissue)
The prominent root has no thick "attached gingiva" which can create health and prevent recession.
|
|
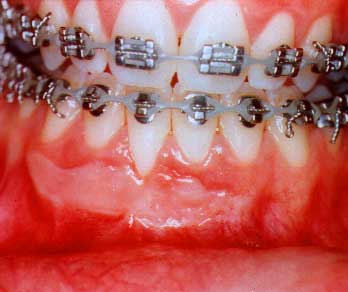
Post-Surgical
There is now thick, tough gum tissue which has partially covered the root and definitely will prevent further recession.
|
|
|
Gum Recession: Bacterial Infection (Periodontitis)
Under a seperate section, we will discuss how gum recession associated with basic gum disease (Periodontitis) is treated. In treating Gum Recession: Bacterial Infection, the recession is a "sign" of a greater problem. In this type of case, our treatments are designed to eliminate the bacterial infection, and don't have much potential to cover existing areas of recession.. While periodontal plastic surgical techniques can sometimes be used with the treatment of this type of recession, most of the recession associated with this type of "bacteria infection" is not the primary focus of treatment since you can't cover this type of recession. Eliminating the gum infection is the primary focus!
|
|
|
|
This www.gumrecession.com website will cover:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Entire Site © 2000 Denisis, Erie, PA, USA
All rights reserved
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

